Lesson 1: Answering Questions
Lesson 1
Answering Questions
AAC Self Study Course

Adapted from Penn State Mentor Project
AAC Self Study Course

Adapted from Penn State Mentor Project
| In this lesson you will learn about answering questions and supporting a young person who uses AAC. |  |
|
 |
|
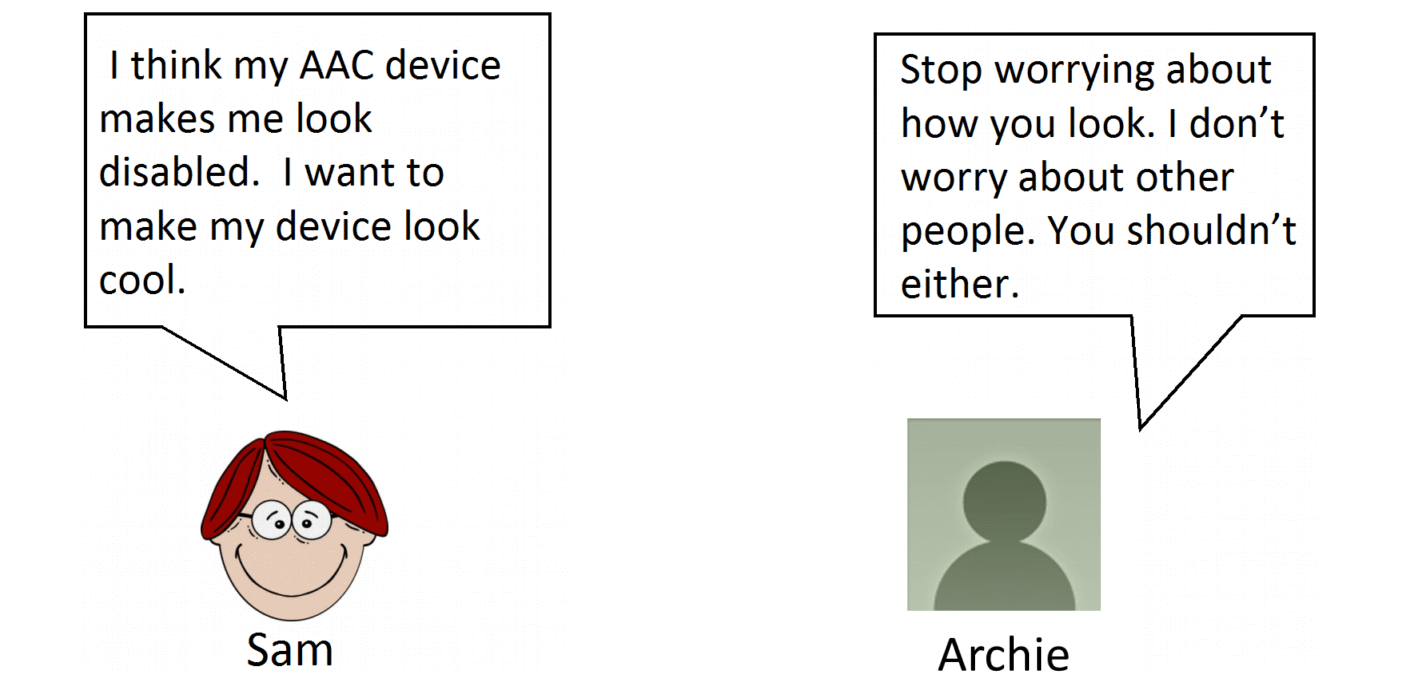
Which of these responses do you think is more effective, Archie's or Matthew's? Let's take a look at each one and break down what is happening in each interaction. |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
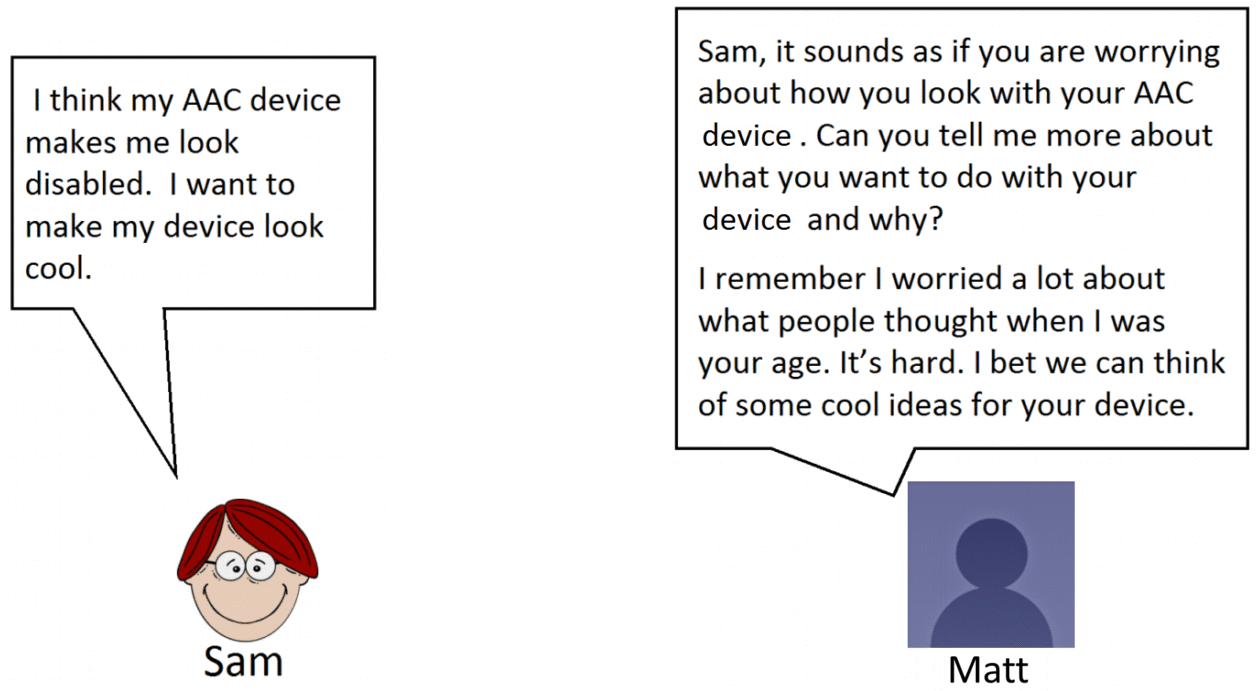
Matt uses good communication skills.
|
|
|
Archie uses poor communication skills.
|
|
|
When you are supporting people who use AAC, it is important for you to:
|
 |
|
 |
| Remember to LAF: | Before you respond, ask yourself: | |
| L | Listen to the person |
Did I listen to the message carefully? Did I show I care? |
| A | Ask questions to better understand |
Did I get enough information to answer? Did I ask good questions? |
| F | Focus on the person | Did my answer show that I am thinking about the other person and how they might feel? |
| Don't CRY: | Before you respond, ask yourself: | |
| C | Don't Criticize | Did I remember not to criticize? |
| R | Don't React too quickly |
Did I think carefully before answering? Did I think about the impact of what I was saying? |
| Y | Don't Yakkity yak! | Did I give the person the chance to communicate everything they wanted to say? |
|
Let's look again at the example of the interaction between the adults and Sam. Matt remembered to use LAF, don't CRY. Let's see how he did it. |
 |

Matt remembers to use LAF. He:
|
 |
Let's do another example...


|
Which of these answers do you think is more effective? Why? Let's take a look at each one and break down what is happening in each interaction. |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
| Sue uses some parts of LAF but doesn't ask questions or encourage Julie to respond. |
Sue |
| Farrah shows she is listening to Julie. She asks questions and focuses on Julie's issue. |
Farrah |
Check to see that you remember the LAF, don't CRY strategy.
Do you remember what these letters stand for:
|
L |
Don't
C |
You have finished lesson 1.
Tell us what you think by completing this quick survey.